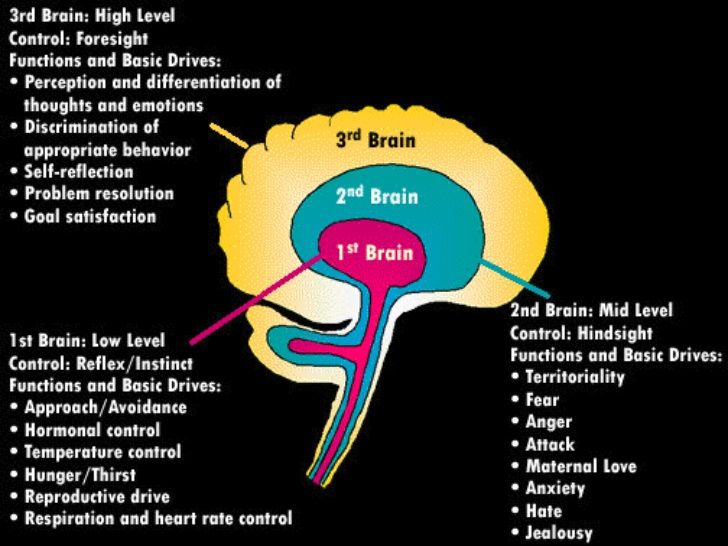
Between the ages of 0 to 24 months a child’s most developed part of their brain is the Lizard brain…Yeah a bit of an unfortunate name, but alas that is what it is called. See picture below for the triune brain lay-out.
Why Do Children Tantrum?
The lizard brain is in control of the survival. Physiological but also external. This part of the brain is also where fight, flight or freeze is located. (Our survival in the great big wild- basically outside of a mother’s womb). When this area of the brain is not triggered, the baby or child’s brain is in limbo and is able to rebuild neural pathways to the rest of the brain.
For a child this young, they cannot discern between need and want, their brain interprets it all as the same. If they need food and cannot have the food, their brain is telling them that they are going to die. Voila child cries and screams to get your attention, so that you respond and baby does not die. When they want a toy, the same feeling of upset triggers the “We are going to die” response and once again baby screams to get what they want.
Delayed gratification development lies within the limbic brain and only starts maturing from the age of 24 months. Thus it is usually recommended that you give a child what they want under the age of 2. We only start practicing delayed gratification and more strict boundaries after they have turned 2.
Biology of a Tantrum
There is also a physiological aspect to the cry that we as parents need to understand as this still plays out in us as adults as well. With the activation of the danger center in the lizard brain the following things happen to the body:
Our body’s blood and oxygen supply route is deliberately changed. Going away from the brain to the larger muscles in the legs and arms. The capillaries narrows in the brain and widen in the muscles during perceived danger. This basically means that any access we had to the frontal lobe has now disappeared and we only have primal instincts to go on.
This results in an actual loss of words. The inability to speak and if we do speak we do so irrationally and almost obsessively repeating the words we have said before the center was triggered.
During this time the ear canal actually closes to only let in low noises. The reason for this connected to when civilization lived in the wild. A creeping lion in the bush will make soft low sounds and our brain needs to be able to hear where it is coming from. When we parent any child of any age during a tantrum, we need to speak to them calmly and in soft hushed voices. They will hear what we say, and the soft calm voice will help them pull back from the perceived danger.
Once our children have calmed down can we try to engage in a short conversation – no more than 3 sentences as to why the boundary is there. Ie, I cannot let you play with the knife. It is dangerous. You can get hurt.
The impact of negative emotions on a child
A child’s main survival instinct is to be close to their parents or primary caregiver. They are completely vulnerable to the outside world, relying on us to help them make sense of the world around them and inside of them. As humans we are wholly flesh and wholly emotions. We use emotions to navigate the world around us. Basically deciding if something is safe by deciding how it makes us feel.
We feel emotions with our whole body, it is not just in our minds, emotions triggers hormones that impact how our body functions. Negative emotions often expressed as a tantrum is something that makes our bodies feel “bad”. Children under the age of 3 perceives this “bad” feeling as a real life threat to them. It becomes a body snatcher as they have little to no control over this reaction. Their brain goes to survival mode and they only know that crying has made the primary caregiver respond quickly. When kids get overwhelmed with the negative emotion, they scream and tantrum.
We see the remnants of the tantrum body snatcher in adults, when we ourselves stomp our feet or clap our hands to draw attention to our frustration or anger. Adults have a fully mature brain and can sense our emotions build up. We should be able to find a safety hatch to redirect our negative emotions too. Kids do not have that – That override switch actually only fully mature at the age of 25.
Why you never walk away from a tantrum
So why should we not walk away or throw a tantrum next to our child when they have a tantrum. Firstly a child has no physical or mental control over how they react. They feel threatened and their brain is telling them that they are actually going to die now. When we walk or run away, or even flop down next to them, expressing the same fear signals they are using. Our kids’ brains interpret this behavior as a sign of danger, we are exactly as scared as what they are.
So fight did not work. They might be immobile or strapped in, so flight isn’t going to work either, the next response then is, freeze. So they fall quiet. The problem is, they are just quiet, still in distress and the hormones that inhibits the oxygen to the brain is even higher. They are now physically preparing to die. This teaches a child that we are unable protect them. There is no reason to trust and believe that this person will be able to protect them.
If you have followed one of these strategies before. I would urge you to stop and rather lean into a tantrum. Allow them to express their fear and anger – remember anger is the gatekeeper of all the negative emotions.
Parenting tantrums in a healthy way
While holding them, if they are not flailing or fighting, whisper calmly that you are there and that you can hear their anger and fear.
Tell them that they are safe and you will not go away from them. They have all the time in the world to work through this emotion. When the tears and crying are done, we can start a rational discussion with our kids.
Join us in our Workshop: Parenting Toddlers (age 0 to 3) Click here and scroll down for more information.
You can also watch this video https://youtu.be/HX7JOEPcP58 on how to parent tantrums in a healthy way.
5,881 total views, 2 views today


Comments are closed.